
toefl.viplgw.cn
- 使用手机注册
- 使用邮箱注册
-
手机号不能为空!
验证码不能为空!
用户名不能为空!
密码不能为空!
-
邮箱不能为空!
验证码不能为空!
用户名不能为空!
密码不能为空!
listen
英['lɪs(ə)n] 美['lɪsn]
vi. 听,倾听;听从,听信
n. 听,倾听

toefl.viplgw.cn
手机号不能为空!
验证码不能为空!
用户名不能为空!
密码不能为空!
邮箱不能为空!
验证码不能为空!
用户名不能为空!
密码不能为空!
英['lɪs(ə)n] 美['lɪsn]
vi. 听,倾听;听从,听信
n. 听,倾听

你的托福备考神器



 立即预约
立即预约

 立即预约
立即预约

 立即预约
立即预约

 立即预约
立即预约

 立即预约
立即预约

 立即预约
立即预约

 立即预约
立即预约

 立即预约
立即预约

 立即预约
立即预约

 立即预约
立即预约











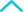


107

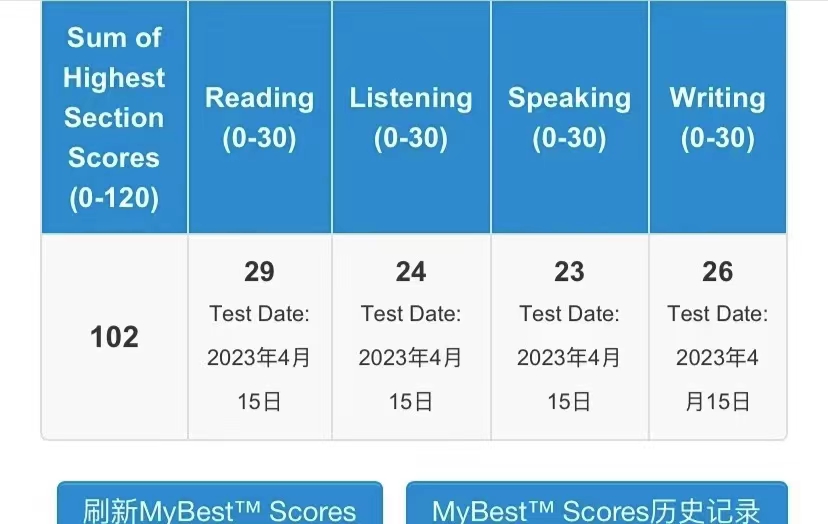
102

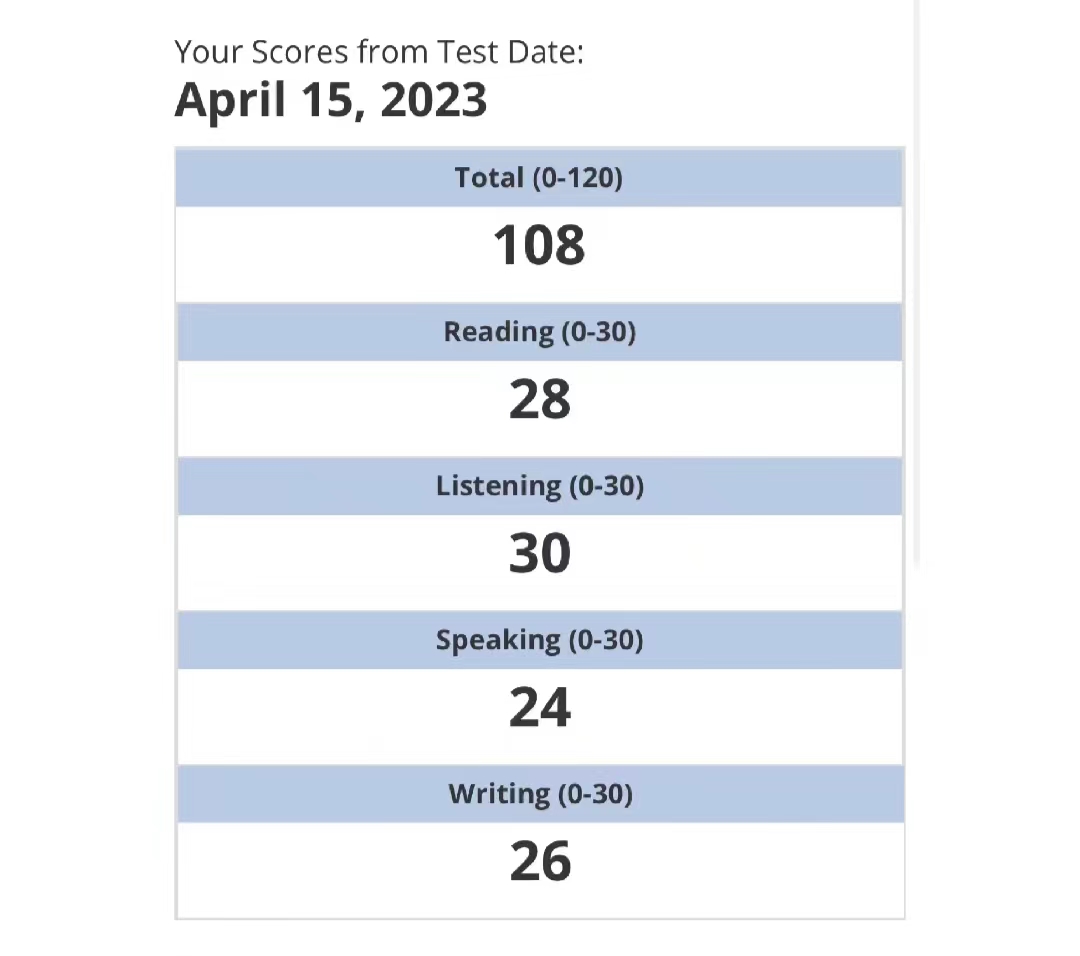
108


100


102

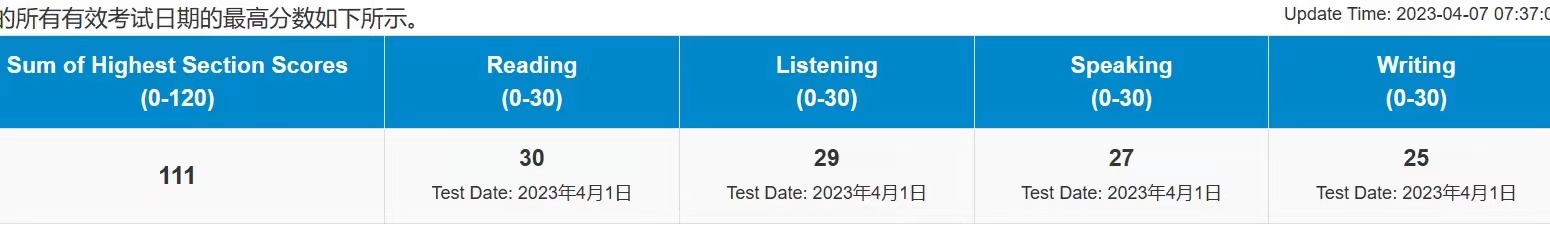
111

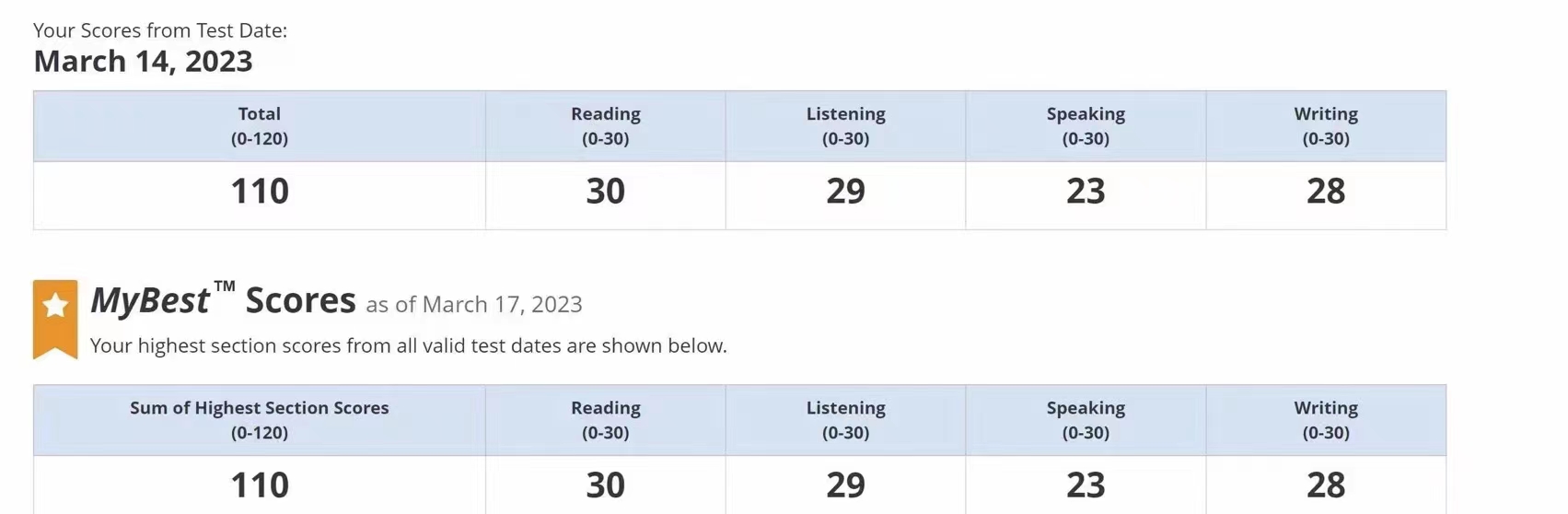
110

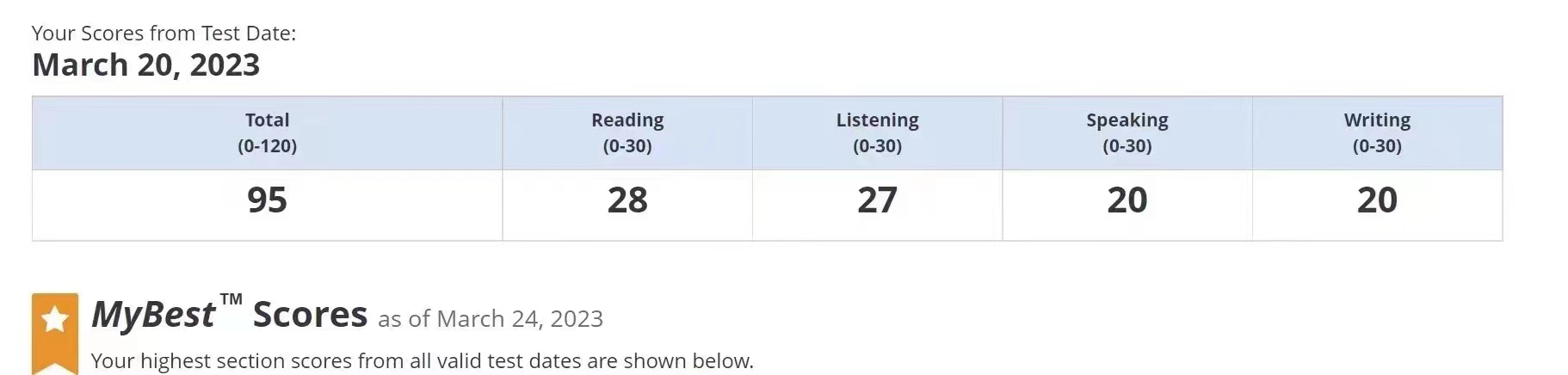
95

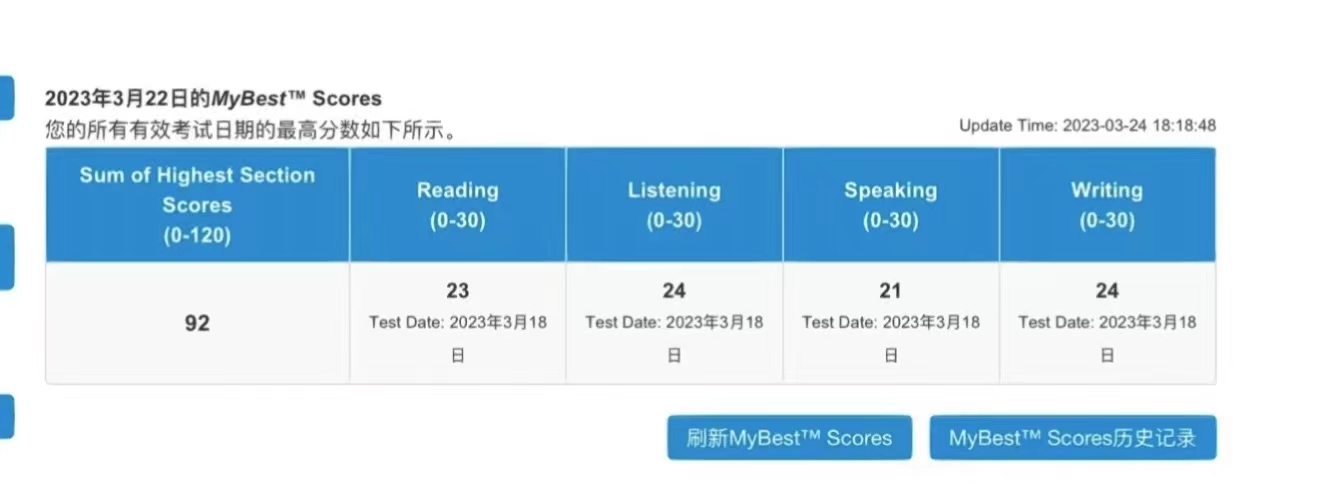
92

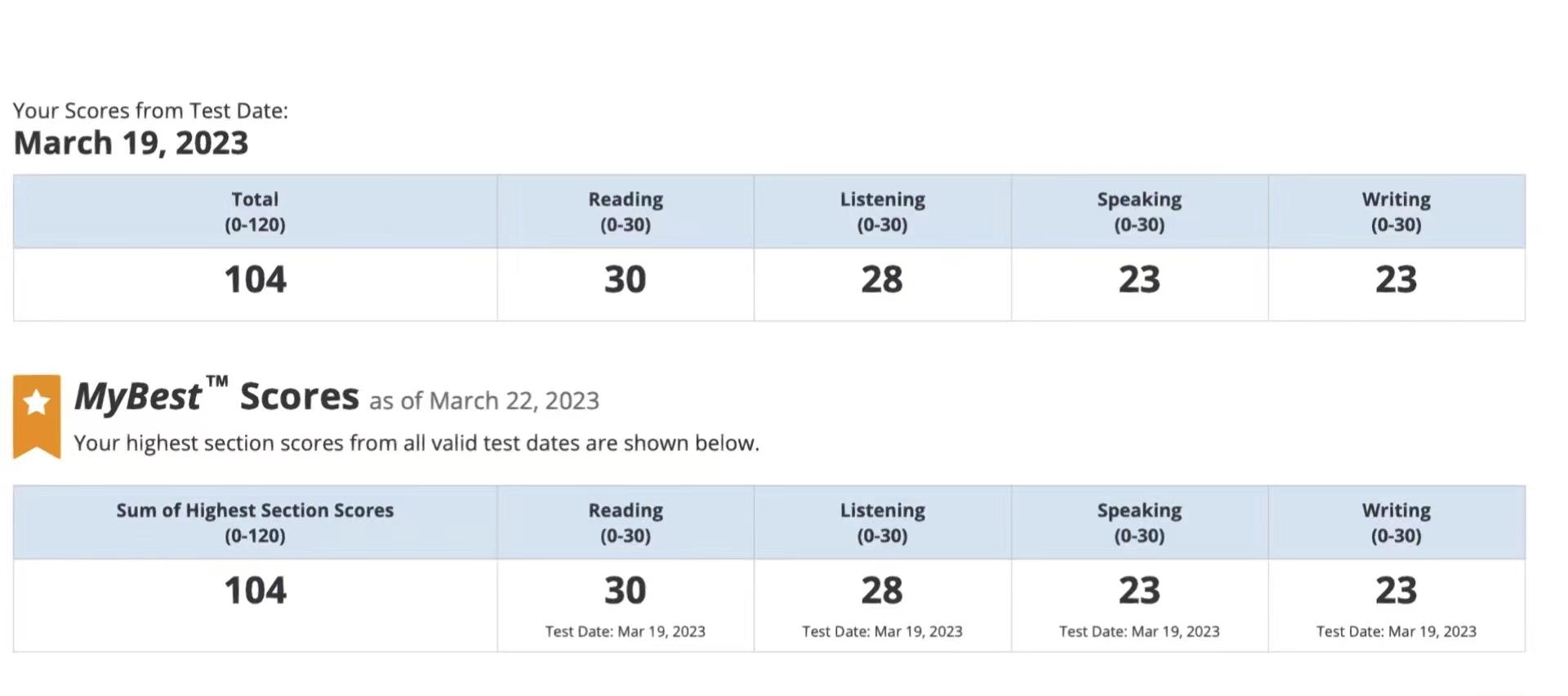
104

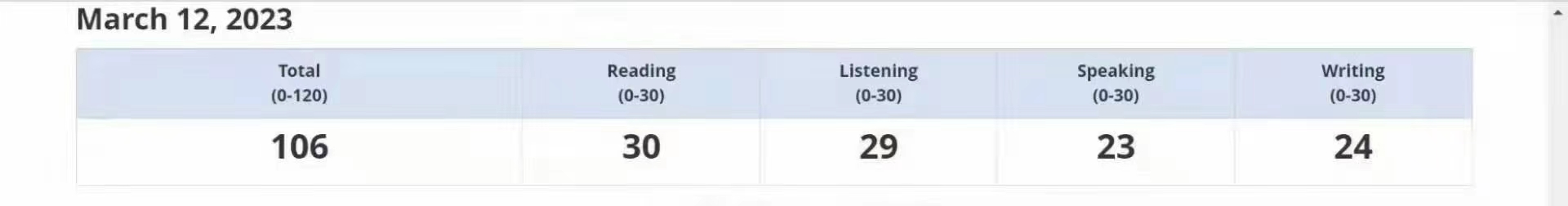
106

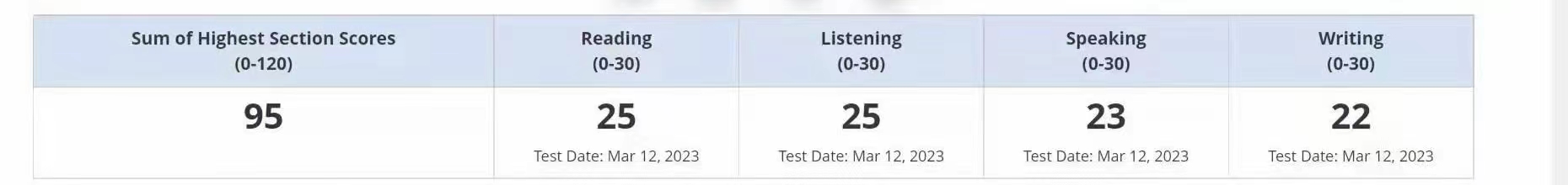
95






 关闭 ( 5s )
关闭 ( 5s )










草莓小菇凉:说的非常好,十分有道理,棒棒棒!
06-08 15:44:55